Blog Search
MALARIA

Malaria is an infectious disease caused by parasitic protozoa.
Its name comes from the words marsh and disease, as it had been observed that the disease was particularly prevalent around marshy areas.
Internationally it is called malaria.
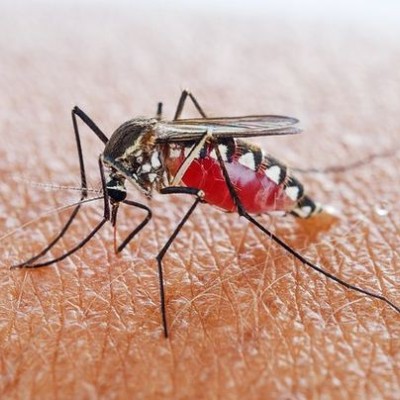
Primarily, the disease is transmitted to humans by the bite of a female mosquito.
Malaria is caused by a microscopic parasite that is usually transmitted by mosquito bites.
The bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into the human blood.
The parasites then travel to the liver, where they mature and reproduce.
But mosquitoes don't have malaria per se.
They simply spread it from person to person, starting with a person who already has malaria.
Less common modes of transmission:
1. transfusion of contaminated blood
2. transplantation
3. contaminated needles
4. from the mother to the fetus during pregnancy
Symptoms usually appear 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
The main ones are the following:
1. Violent shivering that starts suddenly
2. Periodic high fever
3. Sweating
4. Headaches
5. Muscle and joint pains
6. Abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea
7. Exhaustion
8. Anemia
9. Jaundice
10. Convulsions
11. Delirium.
Disease risks can be reduced by preventing mosquito bites by using mosquito nets and insect repellants
or mosquito control measures such as spraying insecticides and draining standing water.
efarmakeio.gr































































































































Αφήστε ένα σχόλιο